Arthritis and arthritis are diseases characterized by pathological changes in the joints, however, the difference between arthritis and arthrosis is significant. To understand the difference between arthritis and arthrosis, it is necessary to consider the etiological factors, pathogenesis, symptoms of arthritis and arthrosis. The treatment of arthrosis and arthritis also has a different approach.
What is arthritis, arthrosis? How are joint lesions shown in arthritis and arthrosis, what is the difference? In arthrosis and arthritis, the difference is due to the mechanism of pathological changes.
Treatment of arthrosis and arthritis is long-term, multicomponent. Often, as a result of untimely treatment, arthritis and arthrosis can be considered as consecutive stages of the pathological process. Having understood what arthritis and arthrosis are, we will determine the difference between arthrosis and arthritis.
Arthritis, classification
Arthritis - caused by inflammatory changes, combines both the pathology of the joint itself, and is a symptom of other diseases that occur with their defeat. How to treat arthritis depends on determining the cause of the inflammatory process.
According to etiological factors, there are:
- Primary - rheumatoid, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Still's disease, others.
- Secondary - complications of infectious, non-infectious processes (reactive with chlamydial infection, hepatitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, septic lesions).
According to the number of affected joints:
- Monoarthritis - with the defeat of one joint.
- Polyarthritis - when a group of joints is affected.
According to the course of the disease:
- Acute arthritis - with a clear clinical picture of inflammatory changes in the connective tissue of the joints.
- Subacute - an intermediate option, the stage of resolving an acute condition.
- Chronic arthritis - with a suppressed clinical picture, a slow course, a period of attenuation and aggravation.
Osteoarthritis, classification
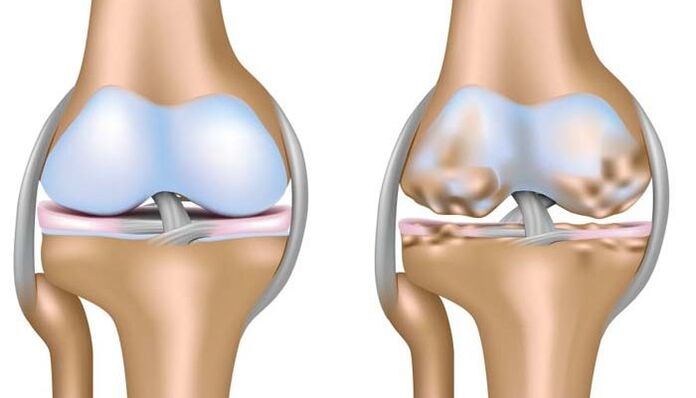
Deforming osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthrosis or arthrosis is a disease based on degenerative changes related to the destruction of all joint structures, cartilage, ligaments, muscles, tendons and bones. This is the main difference between joint arthrosis and arthritis, which leads to irreversible deformity of the affected articular surface, dysfunction, and disability of the patient.
- Idiopathic - no known cause. The pathological process is based on an autoimmune mechanism of damage (primary rheumatoid arthritis in young patients).
- Secondary osteoarthritis is the result of metabolic disorders, trauma, and inflammation. For example, rheumatoid arthritis that develops after experiencing rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis, causes
Risk factors are:
- Violation of metabolic processes in the body.
- Hereditary predisposition factors.
- Contagious disease.
- Immunodeficiency conditions, the presence of autoimmune diseases, allergic manifestations.
- Increased load on the musculoskeletal system due to professional activities, traumatic components.
Arthrosis, causes
Risk factors for developing osteoarthritis are:
- Age. Osteoarthritis is a disease of the elderly, except for rheumatoid arthritis, which occurs in adolescence. According to WHO statistics, about 10% of the world's population suffers from arthropathy.
- Physical stress, injury, excess weight, which increases the load on the joints. Large joints suffer more than others: hip - coxarthrosis, knee - gonarthrosis.
- Hereditary factors: characteristics of metabolic processes, cartilage tissue structure.
- Preceding the inflammatory process without proper therapy.
Arthritis, symptoms
Regardless of the cause of the disease, the signs of the disease have the same clinical picture in the acute phase of the process and during the period of exacerbation of the chronic disease.
- Pain is the first symptom. It has a different intensity, more often it remains, does not depend on physical activity.
- Hyperemia of the skin of the joint area, increased local temperature (the joint area becomes hot to the touch), edema is pronounced.
- The presence of effusion (fluid) in the cavity of the articular bag. Microbiological examination, cytology of fluid from the inflamed cavity is important for diagnosis, establishing causative factors. Knee joints are more often affected. The presence of inflammatory properties of fluid in the joint capsule is the difference between arthritis and arthrosis of the knee joint.
- Extra-articular manifestations of the underlying disease: fever, vascular damage - vasculitis, heart valves, lung disease - alveolitis, pulmonitis, kidney damage - nephritis, skin manifestations, hematological changes - anemia, increased number of peripheral blood platelets.
- Limited range of motion in joints, dysfunction.
Osteoarthritis, symptoms

Symptoms of arthrosis are caused by prolonged malnutrition, blood supply to the cartilaginous plate. Cartilage loses its elasticity, becomes thinner, while growths - osteophytes - are formed from bone tissue in the joint cavity, irreversibly changing the shape of the articular surface, disrupting function, causing pain, and significantly limiting mobility.
- illThe onset of the disease is characterized by moderate intensity, pain, constant pain. The strengthening of the pain syndrome is associated with increased dystrophic changes in the cartilage and deformities. The pain may vary, be temporary: from stiffness in the morning, to constant and subsiding during the day. A rapid and intense increase in pain is a poor prognostic sign.
- visible deformation.
- Functional disorders: flexion, extension.
- Crisp feature when moving.
- Developing joint immobility leads to the disability of the patient.
Osteochondrosis is a common pathological condition of the spine, based on the same changes in cartilage as in arthrosis.
Diagnostics
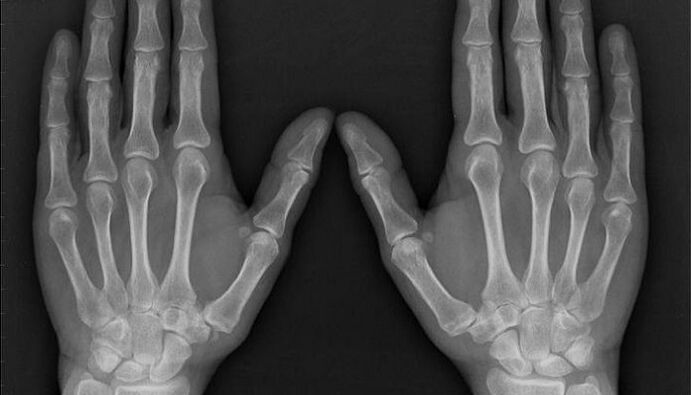
The diagnosis of arthritis and arthrosis aims to identify the cause of the disease, determine the level of activity of the process, evaluate the prognosis and effectiveness of treatment, and diagnose the complications of the disease in a timely manner.
The complex of diagnostic tests includes general clinical laboratory tests, instrumental studies of the liver, kidneys, X-ray diagnostic measures, microscopy, bacteriological studies.
- Distinctive features of arthritis of various etiologies are: an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, an increase in the level of leukocytes in the peripheral blood, which makes it possible to determine the severity of inflammatory changes, an increase in C-reactive protein in the blood plasma - an important laboratory diagnostic test.
- X-ray examination allows you to see characteristic pictures for inflamed articular surfaces.
- MRI is the most informative method for detecting inflammatory changes in the joint capsule.
- Doppler ultrasonography is used.
- In difficult cases, it is possible to perform arthroscopy for the purpose of differential diagnosis and treatment.
A fairly informative method that allows you to establish a diagnosis, distinguishing arthrosis or arthritis, is an X-ray examination. Depending on the identified changes, the degree of intra-articular cartilage deformation and the width of the joint space, four degrees of pathological changes in arthrosis are distinguished.
Arthritis, principles of treatment
Arthritis treatment is long-term, the main goal is to cure the disease that causes inflammatory changes in the joint capsule or achieve a long-term course without disease relapse, prevent the development of irreversible changes, disability, improve the quality and life expectancy of the patient.
For treatment widely used:
- Medical methods of influence. Depending on the etiological factors, the following are used: antibacterial drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormones, the introduction of anti-inflammatory drugs directly into the articular cavity, in the form of severe rheumatic diseases, chemotherapy drugs are prescribed.
- Treatment is not medicine. An important role is played by physiotherapy exercises, diet compliance, healthy lifestyle - stop smoking, alcohol, physiotherapy, timely orthopedic care and correction of existing disorders, prevention of exacerbation of concomitant diseases.
- Surgery is not the preferred method of treatment. This is a way to help patients in very difficult cases - with the development of severe complications, severe pain syndrome, ineffectiveness of the first two methods of treatment. It has certain limitations and indications for appointment.
Osteoarthritis, treatment

Rheumatoid arthritis is treated in a complex, including:
- Therapy is not medicine. In rheumatoid arthrosis, treatment includes physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapy, protective regimen, load reduction, diet, weight loss.
- Medical treatment is associated with pain relief. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal drugs are more often prescribed.
- Surgical treatment methods: plastic, arthrodesis, prosthetics of large joints (knee, hip).
Prevention of exacerbations
Due to the possibility of protracted chronic diseases, the development of complications, regardless of the cause of their occurrence, patients are subject to continuous or long-term observation, rehabilitation measures designed taking into account individual characteristics and properties. the disease.
Important preventive values are:
- Treatment of inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system, a complex of rehabilitation measures after injury.
- Weight restrictions, healthy lifestyle, proper rational nutrition as factors in the fight against overweight.
- Timely orthopedic correction of bone defects acquired in the course of life.
Remember, at the first sign of a problem, it is important to contact a specialist in time. Late treatment initiation increases the risk of possible negative consequences of the disease.



















